Cellulose Products
SCYCLE's Advanced Cellulose Technology Solutions
MicroFibrillated Cellulose
Microfibrillated Cellulose
MFC is a nanomaterial obtained by mechanically microfibrillating cellulose fibers, featuring high aspect ratio, high specific surface area, and excellent mechanical properties.

Applications
Cellulose Nanofiber
Cellulose Nanofiber
CNF is cellulose fiber with nano-scale diameter, maintaining the crystalline structure of cellulose, with extremely high specific surface area and excellent mechanical properties.
Applications

Cellulose Nanocrystal
Nanocellulose Crystal
CNC is highly crystalline nanocellulose obtained through acid hydrolysis, featuring rigid rod-like structure and unique optical properties.

Applications
Technical Specifications
CNF vs CNC Technical Comparison
CNF - Cellulose Nanofiber
Features fiber form, aspect ratio 1/100 or larger
Manufacturing Process: Uses mechanical methods, fiber structure maintains original state
CNC - Cellulose Nanocrystal
Features crystal form, aspect ratio 1/50 or smaller
Manufacturing Process: Produced through acid hydrolysis reaction (treated with sulfuric acid, etc.)
Manufacturing Difference Explanation
The morphological differences between CNF and CNC are caused by their manufacturing methods. Since CNF uses mechanical methods, the fiber structure can maintain its original state; while CNC is produced through acid hydrolysis reaction, where amorphous regions are dissolved by strong acid, leaving only crystalline regions. Although different scholars have varying standards for distinguishing CNF and CNC, they are generally differentiated by shape and aspect ratio (Diameter/Length).
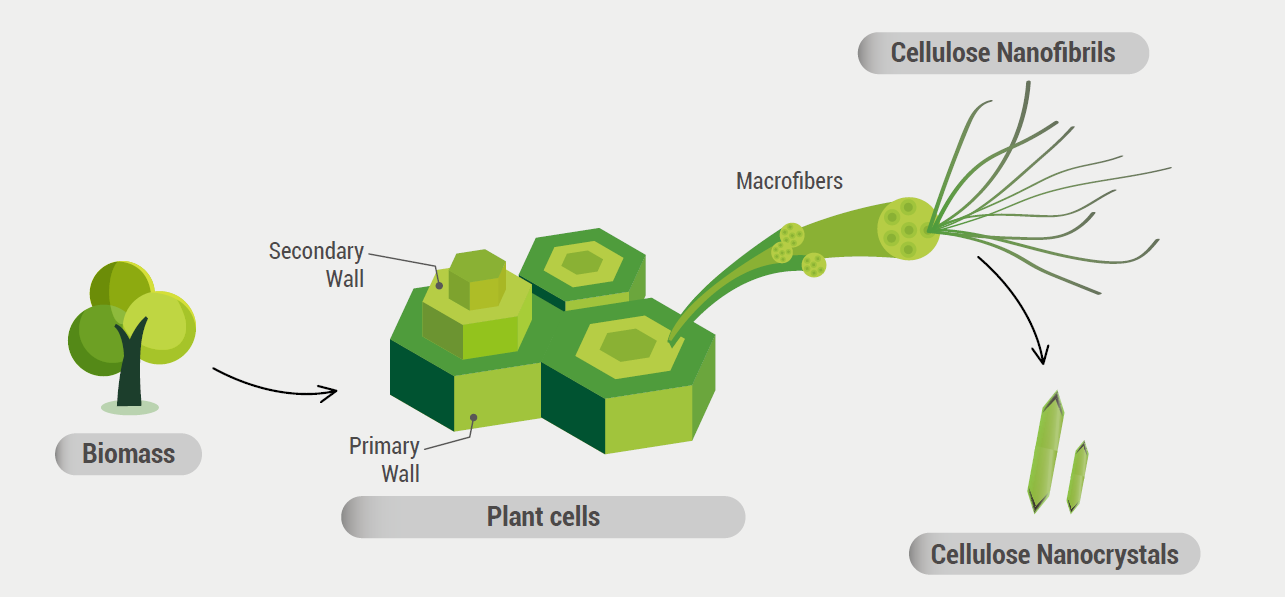
CNF vs CNC Morphological Structure Comparison Diagram
Bacterial Nanocellulose
Bacterial Nanocellulose
BNC is pure nanocellulose produced by bacterial fermentation, featuring unique 3D network structure and excellent biocompatibility.
Applications
